
|
|
back
MENU
|
|
Private
|

Cste power charge
Supercapacitor charging with a constant power
In a first step, the time evolution equations for the supercapacitor charge/discharge are not considering the capacitance dependency over the voltage. With this assumption the imprecision should be smaller than 10%.
Let P be the constant power, C the capacitance, R the series resistance and uc(t) the voltage and u'c its time derivate.
The equation to solve is given by
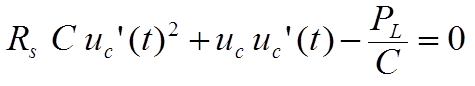
which may be resolved to
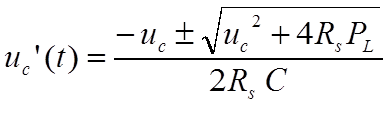
The separation of variables leads to
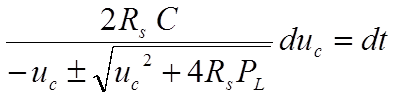
The solution is found after integration. From the 2 solutions only the solution with the "+" is kept.
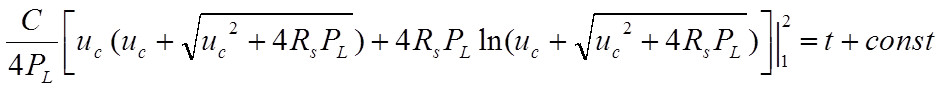
The example below shows the charge and the discharge curves for a BCAP0350 supercapacitor in the case of a constant 20 W power.
From the chart below it's obvious that in order to keep a constant power at low voltage it's necessary to get a high current. This remark leads to the necessity to take care of what is happening at low voltage. In the case of a 20 W application for example, the current below 0.5 V is excessive. More power is burnt in the capacitor internal resistance than in the load.
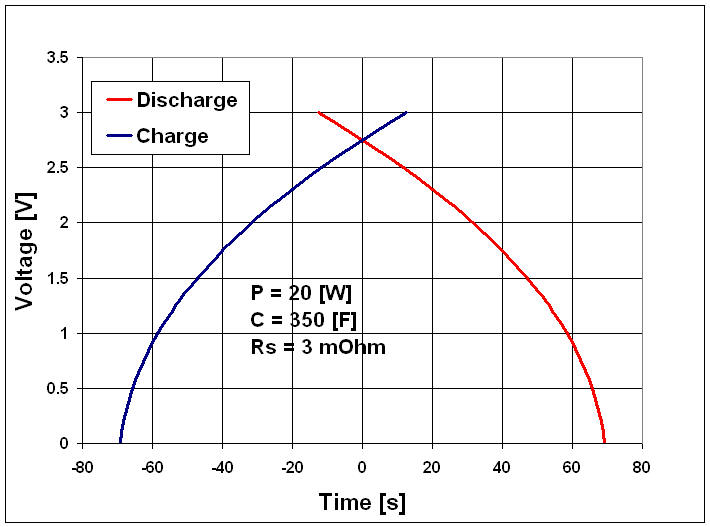
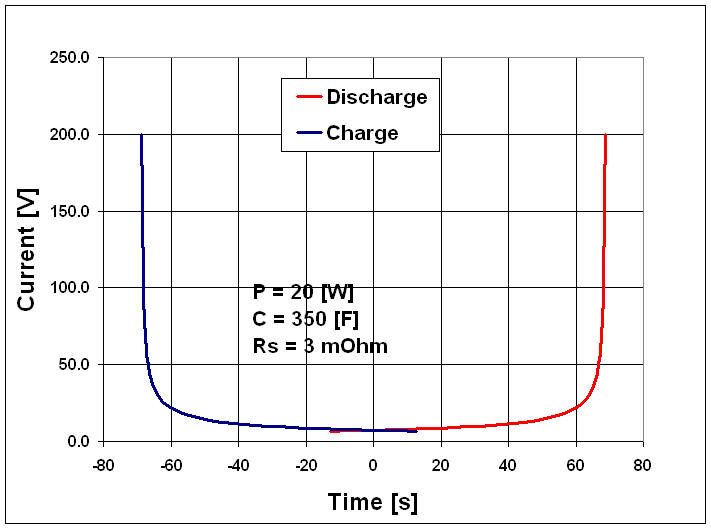
Source: Garmanage, Roland Gallay
