
|
|
back
MENU
|
|
Private
|

Safety
Safety energy reserve for actuators
supercapacitors applications concern the electrical supply of safety systems.
A good example today is the power supply of pitch system in windmill generators. The problem to be solved is to avoid the destruction of the windmill in the case of the absence of load during a network disconnection which leads to an acceleration of the propeller rotation. To remove the wind power, the wings must be reoriented by the pitch system. The request which gives an advantage to supercapacitors in this application is the maintenance free property because the interruption of the energy production has a very high economical impact. Advanced wind turbines consist of three-bladed variable speed turbines. The rotor blades are adjusted and controlled via three independent electro-mechanical propulsion units, the pitch systems. On a pitch controlled wind turbine the rotor blades are slightly turned out of the wind when the power output becomes too high. Conversely, the blades are turned back into the wind whenever the wind drops again. Thus aerodynamic efficiency and reduced loads on the drive train is assured, providing reduced maintenance and longer turbine life. To enhance the level of safety the newest wind turbine technology uses the wind not only to produce energy but also for its own safety. The converters feature aerodynamic braking by individual pitch control. The rotor attains the full braking effect with a 90 degree off position of all blades. Even if a blade pitch unit fails, the braking process is finished off safely by the other two rotor blades. To enhance the level of safety each of the autonomous pitch systems is equipped with an emergency power pack to immediately ensure the reliable functioning of the pitch system, for example in the event of a total power failure or for maintenance purposes. Due to their high reliability, efficiency and operating lifetime, supercapacitors have been designed into pitch systems of many wind turbine manufacturers and pitch system designers.
Pitch systems are located in the rotating rotor hub of the wind turbine (Fig. 1).
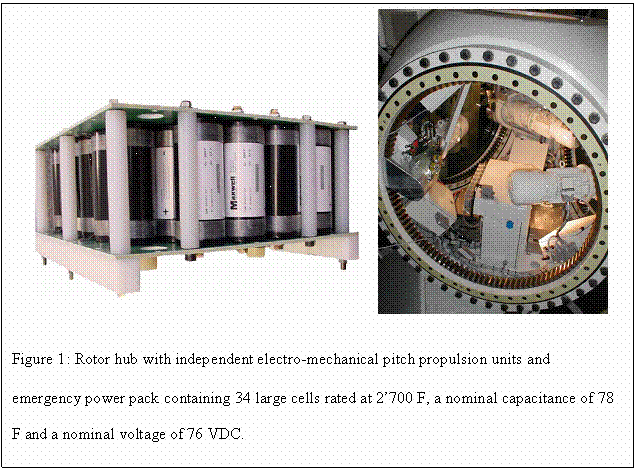 The power supply and control signals for the pitch
systems are transferred by a slip ring from the non rotating part of the
nacelle. The slip ring first is connected to a unit which includes clamps for
distributing power and control signals to the three individual blade drive
units. Each of them consists of a switched mode power supply, a field bus, the
motor converter, an emergency system, and the supercapacitor bank. When the power
supply is switched on, the supercapacitor module is charged to its nominal voltage.
Typical charging time is approximately 1 minute. The capacitor module has an energy
content high enough to run the system for more than 30 seconds with nominal
power. The supercapacitor module is directly connected to the DC link of the motor
converter.
The power supply and control signals for the pitch
systems are transferred by a slip ring from the non rotating part of the
nacelle. The slip ring first is connected to a unit which includes clamps for
distributing power and control signals to the three individual blade drive
units. Each of them consists of a switched mode power supply, a field bus, the
motor converter, an emergency system, and the supercapacitor bank. When the power
supply is switched on, the supercapacitor module is charged to its nominal voltage.
Typical charging time is approximately 1 minute. The capacitor module has an energy
content high enough to run the system for more than 30 seconds with nominal
power. The supercapacitor module is directly connected to the DC link of the motor
converter.
Megawatt class turbines dominate much of the actual world market, pushing the development of multi-megawatt turbines, as the offshore market may demand such installations. The largest turbines are able to produce power up to 5 MW with a rotor diameter of up to 110 m ensure the functioning of the fast blade pitch system even for such large installations, bigger emergency power packs have to be integrated.
Source: Garmanage: Roland Gallay